Difference between ROLAP, MOLAP and HOLAP
Learn about the 3 types of OLAP engines: Relational OLAP, Multidimensional OLAP and Hybrid OLAP
Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) was introduced a couple of decades ago. Computation power was limited and business scaling was difficult without hardware replacements.
However, introducing OLAP was groundbreaking in the Business Intelligence industry. Users could perform multidimensional analysis on large volumes of data.
Before integrating OLAP, it was always challenging to run queries on a Data Warehouse. Drawing data from multiple tables was always tedious. The execution of these queries took long periods of time to complete and often affected the overall system performance.
By introducing OLAP, these problems were resolved by pulling data out of the data warehouse. All aggregate measures were pre-computed at every level for every dimension to build the multidimensional cubes.
This helped quicken report running and enabled business users to run ad hoc queries, slice and dice data, drill down and mine data for uncovering patterns, and better analyse the data sets.
There are three types of OLAP engines: Relational OLAP (ROLAP), Multi-dimensional OLAP (MOLAP), and Hybrid OLAP (HOLAP).
Relational Online Analytical Processing (ROLAP)
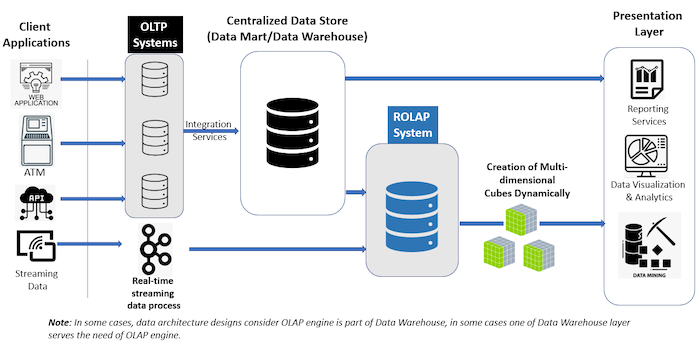
ROLAP allows for relational database data storage as rows and columns. It then dynamically presents the data to the end user in multidimensional cubes.
Data can be accessed by submitting queries to the ROLAP database.
 ROLAP
ROLAP
Large volumes of data can be processed but the performance of the query is largely dependent on the size of the data retrieved. With an increase in data, comes the less accurate query performance.
Multi-dimensional Online Analytical Processing (MOLAP)
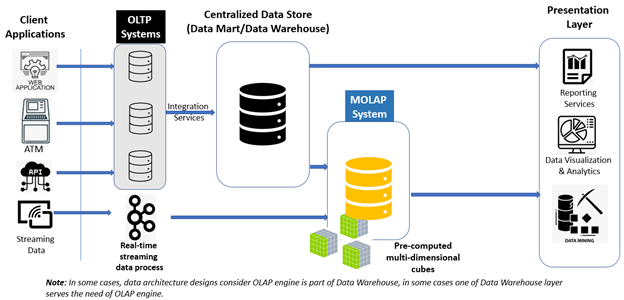
MOLAP retrieves its data from a Centralised Data Store (Data Warehouse/Data Mart) and other designated sources. It pre-computes all aggregate measures at every dimensional level to build the multidimensional cubes. After processing, the data is stored in MOLAP's database.
 MOLAP
MOLAP
Business users can also access the multidimensional data for further analysis and reporting. Queries on MOLAP's database generally run faster due to batches of pre-computation processes applied.
Hybrid Online Analytical Processing (HOLAP)
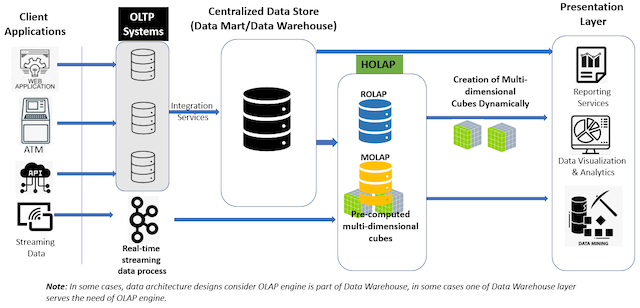
HOLAP combines the capabilities of MOLAP and ROLAP to support its use cases.
HOLAP has a combination of pre-computed multidimensional cubes in MOLAP's database and relational data in ROLAP's database to support the various use cases of end users.
 HOLAP
HOLAP
HOLAP stores data (multidimensional data and relational data) required by business users in its system.
Decisions have to be made to configure access for each OLAP system to suit your needs. All OLAP use cases have a predefined configuration for access and the ability to run queries.
Also read: What is ClickHouse? (A fast open-source OLAP DBMS)
About the author: Sudarsan is a customer solution architect at ByteDance; and, he is a CDMP (DAMA) certified data architect with prior experiences with National University of Singapore, Development Bank of Singapore, Standard Chartered Bank and BNP Paribas.